Every time ImaginaTIon Technologies is mentioned, my colleagues in my field will think of PowerVR and MIPS - the two major brands of GPU and CPU space.
However, ImaginaTIon's reputation began to rise, relying on its achievements in the wireless market Ensigma, a powerful connection technology.
One of Ensigma's features is its ability to support a wide range of wireless standards, including 802.11 b/g/n/ac Wi-Fi, conventional low-power Bluetooth, digital TV and radio broadcasting, and Cat 0 LTE.
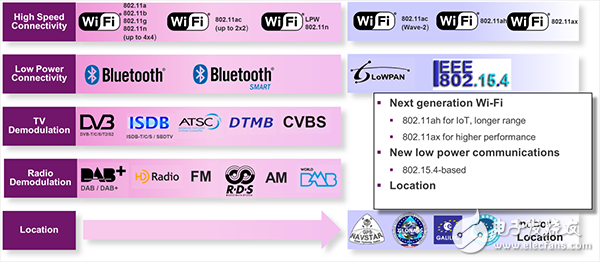
The multiple standard approach reflects a trend that has a greater impact on the wireless market: heterogeneous connectivity. This is especially true when it comes to next-generation wireless standards such as 5G. In the 5G era, we will see a combination of standards to get a true uninterrupted connection.
What is a heterogeneous connection?
When people talk about 5G, the first thing that comes to mind is that this will be another cellular standard. This is mainly because the main driving force of 5G is the 3GPP Foundation, a project that combines multiple cellular organizations.
However, I don't think 5G is just a cellular standard for the following reasons. First, in the original specification, 29 candidate bands were considered to be 5G. Currently, some existing frequency bands are being deployed – 900 MHz and 1800 MHz are the most obvious examples. Other new bands, such as 700 MHz and 600 MHz, are also beginning to emerge. Finally, some bands are using unauthorized portions of the spectrum. One example is the release 13 version of the 4 GB standard, which targets the 5 GHz LTE space, LTE-AA.

It is not surprising that some companies are also looking for millimeter waves (above 18 GHz, especially the 60 GHz unlicensed spectrum). At the same time, I have also seen some 5G field tests, which also use millimeter waves of 29 GHz.
So at this point, it is not certain whether there is a specification or standard between 600 MHz and 63 MHz.
What is cognitive connection?
A simple example can quickly understand the meaning of cognitive connectivity, the decision of the FCC and its allowed providers to share the 3.5 GHz to 3.7 GHz portion of the spectrum. This is a way similar to the TV white space spectrum, which I have previously introduced.
A cognitive device that shares a spectrum needs to know its location and access the spectrum information of the database. The database will tell the device which channels they can operate or use.
These two requirements (location identification and database access) essentially define the cognitive approach to connectivity.
If these principles are applied to next-generation systems, we will find that there will be a range of potentially available channels and spectrum. When a mobile phone switches wireless functions, there may be a 29-bit spectrum, so it requires sensible thinking.
By using GPS or other location identification, the mobile device will determine which part of the search signal is needed. For example, if you travel from the US to Europe or Asia, your phone can get signals from different spectrums.
Devices also need to know which ones can coexist in the spectrum. If the 5 GHz band is available, you can use high-speed Wi-Fi or some type of cellular connection. If it is in the 2.4 GHz range, you can choose low-power Wi-Fi or even Bluetooth. For 915 MHz, it can be an 802.15.4 based technology (eg 6LoWPAN).
The fastest speed does not mean that wireless services are the best. With 5G, we need to start thinking about the capabilities of the network.
What people expect is that whether they are in London or North American National Park, they use a mobile phone, laptop, tablet or other mobile embedded device to help with a specific task.
If they want to send an email, they want the email to work quickly. If they want to watch the video, they want a smoother user experience. This means that the network has begun to make more informed decisions because many users have very different needs.
For example, if a group of users is only dealing with text-based email, they do not theoretically need access to high-bandwidth technologies. For video, the network must be able to get the latest high-speed cellular connections, and the importance of speed is irreplaceable.
Currently, some US and UK carriers using 4G are also beginning to offer Wi-Fi voice calls. If you can't get a cellular connection, and you have Wi-Fi, you can still use Wi-Fi calls.

In the future, the scope of this cognitive connectivity application will be expanded, thanks to the Internet of Things market.
As for whether there are small IoT sensors or high-performance mobile devices, ImaginaTIon has invested in Ensigma to ensure it can provide a scalable solution to meet the needs of all these different markets.
1.The strong technology group as well as the advanced equipment;
2.More than 40 years casting experience;
3.The Products have got good comments in the world market;
4.OEM service and special design service be accepted;
5.ISO9001-2008 Certified.
Pulley is the important tools for hoisting. It has simple structure and easy to use. It can change direction of
pulley, steel wire rope and high weight cargoes, especially series of pulley combined with windlass, mast and other lifting machinery.
It widely used in installation and construction. Its item from 0.03T to 320T, and wheels not exceed ten.
Our lifting tools including hooks, chain lifting ring and handing beam, you can choose one according to your need.

Pulley Block, Stringing Block, Nylon Pulley
NINGBO BEILUN TIAOYUE MACHINE CO., LTD. , https://www.spool-manufacturer.com