Wireless communication devices, when operating at their highest power levels, can generate significant electromagnetic interference (EMI) that may affect nearby electronic equipment. Among these, the interference caused to hearing aids used by individuals with hearing impairments is particularly critical, as it can directly disrupt the normal functioning of the users. To address this issue, the ANSI C63.19 standard outlines specific test requirements for Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC). Within this standard, the measurement of both RF electric field and RF magnetic field radiation from wireless devices plays a crucial role in evaluating their impact on hearing aids. In this section, we will provide an overview of the methods used to measure these two types of radiation.
The HAC testing process typically involves several key instruments, including:
1. Near-field electric field probe;
2. Near-field magnetic field probe;
3. Probe positioning system;
4. Wireless Device (WD) support system;
5. Additional equipment such as an RF shielding chamber.
During the test, the wireless device must be set to its maximum rated output power, and the test should be conducted across high, medium, and low frequency channels. It is essential to ensure that all measuring equipment, including the field strength probes and the test system, are functioning correctly. The probe position must be precisely calibrated and aligned to maintain accuracy throughout the process.
The HAC test is performed within a 5 cm area, where the electric field probe scans the surface to detect the maximum field strength. This is done over multiple pulses, using peak measurements, and then the average field strength is calculated based on the measured value and a constant duty cycle. To ensure comprehensive coverage, the center of the probe must be scanned across the entire test area. The distance between the probe element and the reference plane of the object under test should be maintained at 1.0 cm.
A simplified version of the test procedure is illustrated in Figure 1 below:
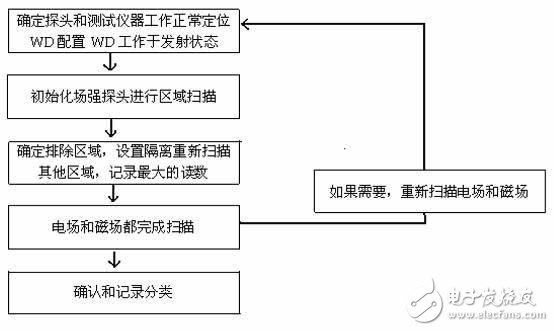
Brief Test Flow
The final test result is represented as the maximum peak reading, which is then converted into equivalent peak values in volts per meter (V/m) or amperes per meter (A/m). These measured values are compared against the limits specified in the ANSI C63.19 standard to determine the compatibility level.
Additionally, the ANSI C63.19 standard provides detailed procedures and classification methods for assessing the electromagnetic compatibility between hearing aids and digital mobile phones. Different models are tested and categorized into four levels: 1, 2, 3, and 4. When both the hearing aid and the mobile phone are rated at level 4, the resolution index reaches 0.3, which is acceptable for basic communication. If the sharpness index exceeds 5, the performance is considered good, allowing for normal use. When the sharpness index is 6 or higher, the call quality is considered excellent, with a sharpness index of 0.7.
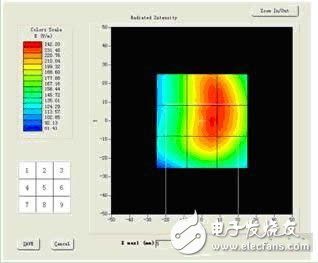
Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing and Classification Methods
Diamond Saw Blade Testing Machine
Diamond Saw Blade Testing Machine,Saw Blade Stress Testing Machine,Welding Accuracy Test Machine,Saw Blade Torque Test Machine
Suzhou Mountain Industrial Control Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.szmountain.com