The function of assigning the virtual MAC address of the master router described above enables different hosts to send traffic to different routers in the backup group. However, in order to enable routers in the backup group to forward traffic sent by the host, a virtual forwarder needs to be created on the router. Each virtual forwarder corresponds to a virtual MAC address of the backup group and is responsible for forwarding the traffic whose destination MAC address is the virtual MAC address.
This article refers to the address: http://
1. Virtual forwarder creation
The virtual forwarder is created as follows:
(1) After the router in the VRRP group obtains the virtual MAC address assigned to the master router, it creates a virtual forwarder corresponding to the MAC address. The router is called the virtual forwarder VF Owner (VirtualForwarder Owner) corresponding to the virtual MAC address. , virtual forwarder owner).
(2) The router advertises the information of the virtual forwarder to other routers in the backup group.
(3) After the other routers in the backup group receive the virtual forwarder information sent by the router, the virtual forwarder corresponding to the virtual MAC address is created locally.
It can be seen that the router in the VRRP group needs to create a virtual forwarder corresponding to the virtual MAC address assigned by the master router, and a virtual forwarder corresponding to the virtual MAC address advertised by other routers.
2. The weight and priority of the virtual forwarder
The weight of the virtual forwarder identifies the forwarding capability of the router. The higher the weight value, the stronger the forwarding capability of the router. When the weight is below a certain value - the lower limit of failure, the router can no longer forward traffic for the host.
The priority of the virtual forwarder is used to determine the status of the virtual forwarder. The virtual forwarder with the highest priority is in the active state, called the AVF (Active Virtual Forwarder). Responsible for forwarding traffic; other virtual forwarders are in the Listening state, called LVF (Listening Virtual Forwarder), which monitors the state of the AVF. The priority of the virtual forwarder ranges from 0 to 255, of which 255 is reserved for use by the VF Owner. If the weight of the VF Owner is higher than or equal to the lower limit of failure, the priority of the VF Owner is the highest value of 255.
The rules for the device to calculate the priority of the virtual forwarder based on the weight of the virtual forwarder are as follows:
If the weight is higher than or equal to the lower limit of failure and the device is VF Owner, the priority of the virtual forwarder is the highest value of 255.
If the weight is higher than or equal to the lower limit of failure and the device is not a VF Owner, the priority of the virtual forwarder is weight / (number of local AVFs +1).
If the weight is below the lower failure limit, the virtual forwarder has a priority of zero.
3. Virtual forwarder backup
A backup relationship is formed between multiple virtual forwarders corresponding to the same virtual MAC address on different routers in the backup group. In the example shown in Figure 4-9, the virtual forwarder information and its backup relationship on each router in the backup group are described.
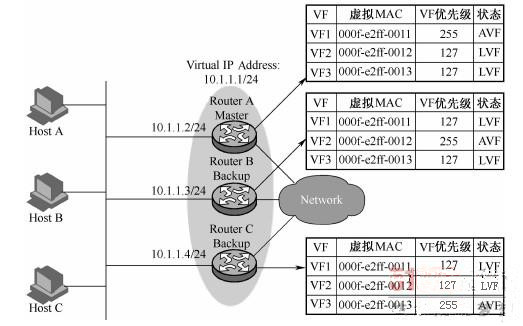
Figure 4-9 Virtual forwarder backup in load balancing mode
In this example, the virtual MAC addresses assigned by Router A to Router B and Router C are 000fe2ff0011, 000fe2ff0012, and 000fe2ff0013, respectively. The virtual forwarders corresponding to the virtual MAC address are VF1, VF 2, and VF 3. The three virtual forwarders are created on Router A, Router B, and Router C, and form a backup relationship. For example, VF 1 on Router A, Router B, and Router C back up each other:
Router A is the VF Owner of VF 1, and the virtual forwarder of VF 1 on Router A has the highest priority of 255. Therefore, VF 1 on Router A acts as the AVF and forwards the traffic with the destination MAC address being virtual MAC address 000fe2ff0011.
The priority of the virtual forwarder of VF 1 on Router B and Router C is 255 (the number of local AVFs +1) = 127, which is lower than the priority of VF 1 on Router A. Therefore, VF 1 on Router B and Router C is used as the LVF to monitor the status of VF 1 on Router A.
When VF 1 on Router A fails, the LVF with the highest priority of the virtual forwarder is elected as the AVF from the VF 1 on Router B and Router C. The traffic with the destination MAC address being the virtual MAC address 000fe2ff0011 is forwarded.
[Description] The virtual forwarder always works in preemption mode. For LVFs and AVFs that are backed up on different routers, if the LVF receives the virtual forwarder priority of the virtual forwarder information sent by the AVF, the LVF will preempt to become the AVF.
4. Virtual repeater timer
After the AVF of the virtual repeater fails, the new AVF that takes over its work will create two timers, Redirect Timer and Timeout Timer, for the VF.
Redirect Timer: VF redirection timer. Before the timer expires, the master router will respond to the host's ARP/ND request with the virtual MAC address corresponding to the VF. After the timer expires, the master router no longer responds to the host's ARP/ND with the virtual MAC address corresponding to the VF. request. If the VF Owner recovers before the Redirect Timer expires, the VF Owner can quickly participate in traffic load balancing.
Timeout Timer: The VF survival timer, which is the period during which the AVF takes over the work of the VF Owner. Before the timer expires, the VF is reserved on the router in the backup group. The AVF is responsible for forwarding packets with the destination MAC address being the virtual MAC address of the VF. After the timer expires, the VF is deleted on the router in the backup group. The packet whose destination MAC address is the virtual MAC address of the VF is not forwarded.
5. Virtual forwarder monitoring function
The AVF is responsible for forwarding the traffic whose destination MAC address is the virtual forwarder MAC address. If the uplink of the AVF connection fails, if the LVF cannot be notified to take over the work, the host with the virtual forwarder MAC address as the gateway MAC address in the local area network. You will not be able to access the external network.
The monitoring function of the virtual repeater can solve the above problem. The NQA (Network Quality Analyzer) and the BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) are used to monitor the uplink status of the AVF connection. The track function is used to establish a linkage between the virtual forwarder and the NQA/BFD. When the uplink fails, the status of the track entry changes to Negative, and the weight of the virtual forwarder decreases by the specified amount, so that the router with higher priority of the virtual forwarder preempts the AVF and takes over the forwarding traffic.
The virtual repeater monitoring function can also be used to monitor the status of the AVF via Track on the LVF. When the AVF fails, the LVF operating in the virtual repeater fast switching mode can quickly become the AVF to ensure that the communication is not interrupted.
Multi-layer PCB is the printed circuit board that the copper layer equal or beyond 4layer. For example, we could do 1-36layer PCB, so 4-36layer PCB are all Multilayer PCB. For multilayer PCB, the copper thickness of each layer could be same and also could be different, it's based on the layer stack-up. And normally, multilayer PCB may require impedance control.
How Are Multilayer PCBs Made?
Alternating layers of prepeg and core materials are laminated together under high temperature and pressure to produce Multilayer PCBs. This process ensures that air isn't trapped between layers, conductors are completely encapsulated by resin, and the adhesive that holds the layers together are properly melted and cured. The range of material combinations is extensive from basic epoxy glass to exotic ceramic or Teflon materials. The figure above illustrates the stackup of a 4Layer/ multilayer PCB. Prepeg and core are essentially the same material, but prepeg is not fully cured, making it more malleable than the core.The alternating layers are then placed into a lamination press. Extremely high temperatures and pressures are applied to the stackup, causing the prepeg to "melt" and join the layers together. After cooling off, the end result is a very hard and solid multilayer board.
-Higher assembly density
-Smaller size (considerable savings on space)
-Increased flexibility
-Easier incorporation controlled impedance features.
-EMI shielding through careful placement of power and ground layers.
-Reduces the need for interconnection wiring harnesses (reduces overall weight)
PCB Manufacture Capabilities
|
Features |
Capabilities |
|
Layers |
1-36 layers |
|
Material |
FR-4, Aluminum, Copper, Polyimide, high frequency (Rogers, PTEE, PI), etc. |
|
PCB Type |
FR-4 Standard PCB, Aluminum PCB , Copper-based PCB, HDI PCB , Rigid-Flex PCB, Flex PCB, Thick Copper PCB and Rogers PCB, etc. |
|
Board Thickness |
0.1mm-6.0mm |
|
Copper Thickness |
1/2oz-6oz(18um-210um) |
|
Biggest Board size |
600mm*1200mm |
|
Min Tracing/Spacing |
0.075mm/0.075mm (3mil/3mil) |
|
Min drilling Hole diameter |
0.15mm(6mil), 0.1mm(4mil)-laser drill |
|
Solder Mask |
Green, Black, White, Red, Yellow, Blue and Purple, etc. |
|
Silkscreen color |
White, Blue, Black, Red, Yellow |
|
Surface finish |
HASL Lead free, Immersion Gold (ENIG), Immersion Tin, Immersion Silver, OSP, Carbon oil, etc. |
|
Special Techniques |
Impedance Control, Gold Fingers, Blind/Buried vias, Peelable solder mask, Half holes, Via-in-Pad and Countersink hole, etc. |
PCB Products Show
PCB Factory Show

Multilayer PCB
Multilayer PCB,Multilayer PCB Board,Multilayer PCB Design,Multilayer PCB Prototyping
ZhongFeng Electronic Technology Co., Limited , https://www.dopcba.com